
一种基于海藻酸水凝胶的人原代胰腺癌细胞培养平台,结合了浓度梯度生成器,用于药物评估。
Introduction
思路:
胰腺癌是最致命的癌症之一,外科切除是目前的首要策略。基于化疗(如吉西他滨和氟尿嘧啶)的术后辅助治疗也常被联用,为了提高病人无进展生存期。然而由于不同个体的肿瘤异质性,治疗结果常常不尽如人意,临床人员往往要根据经验对不同的病人用药。鉴于此,需要一个有效的药物平台用于体外模拟胰腺癌药物响应,以指导临床用药。
作者提出了一个基于微流控水凝胶胶囊的人原代胰腺癌细胞培养平台,能形成3D仿生肿瘤球用于药物评估,如图1。当前:
- 不同于传统2D培养,3D肿瘤球具有肿瘤细胞和细胞外微环境的双向相互作用能力;
- 当前的肿瘤球通常在简单的孔中培养,缺乏外部限制;
- 肿瘤尺寸的异质性和来源于细胞系的肿瘤球不足以模拟不同个体的肿瘤变异性;
- 营养和药物摄取的动态供应难以在当前3D肿瘤模型中达成。
微流控技术可以精确地操纵集成通道中的微尺度流体,从而实现系统中可控的营养供应或药物分布。同时,微流控技术可以生成具有可调节的、统一尺寸形状和定制的微结构的功能性微颗粒或微胶囊,用于细胞封装和3D培养。因此,设想通过整合三维肿瘤模型和微流控技术的优势,开发一个具有预期功能的药物评估的有效平台。
基于此,作者提出了基于微流控电喷技术,用于将人原代胰腺癌细胞封装在水凝胶微胶囊中进行3D培养。微胶囊由羧甲基纤维素(carboxymethyl cellulose,CMC)核和海藻酸盐(alginate,ALG)壳组成:
- 具有高均匀性、稳定性和精确的尺寸控制,同时它们也具备良好的生物相容性和可获得性。
- 此外,相比于光聚合,海藻酸钠的离子交联过程简单、快速以及对包裹细胞伤害更小。
得益于这些性质,封装的原代胰腺癌细胞能在半渗透的水凝胶胶囊中快速增殖和自发形成高度尺寸均匀和良好细胞活性的3D肿瘤球。交联的水凝胶展示了一定的机械强度,不易崩解,有助于药物筛选所需的肿瘤球的长期稳定性。通过将这些封装的肿瘤球整合到带有梯度发生器和培养室的微流控芯片中,可以实现对不同化疗方案的动态和高通量药物评估。从封装的肿瘤球中获得的数据和从相应的病人获得的对化疗药物反应的临床数据之间有明显的一致性。结果表明,3D肿瘤模型和微流控技术的整合可以为胰腺癌的临床治疗提供一个可靠和准确的药物评估平台。
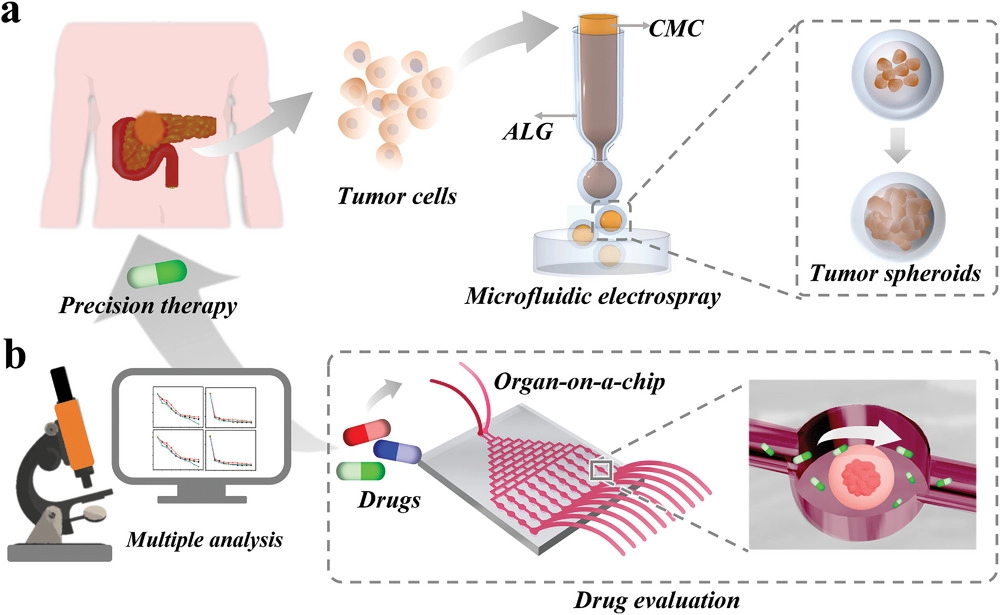
- (a)包裹肿瘤球的水凝胶微胶囊的设计。
- (b)用于药物评估的微胶囊集成芯片。
Preparation and regulation of the CMC/ALG microgels
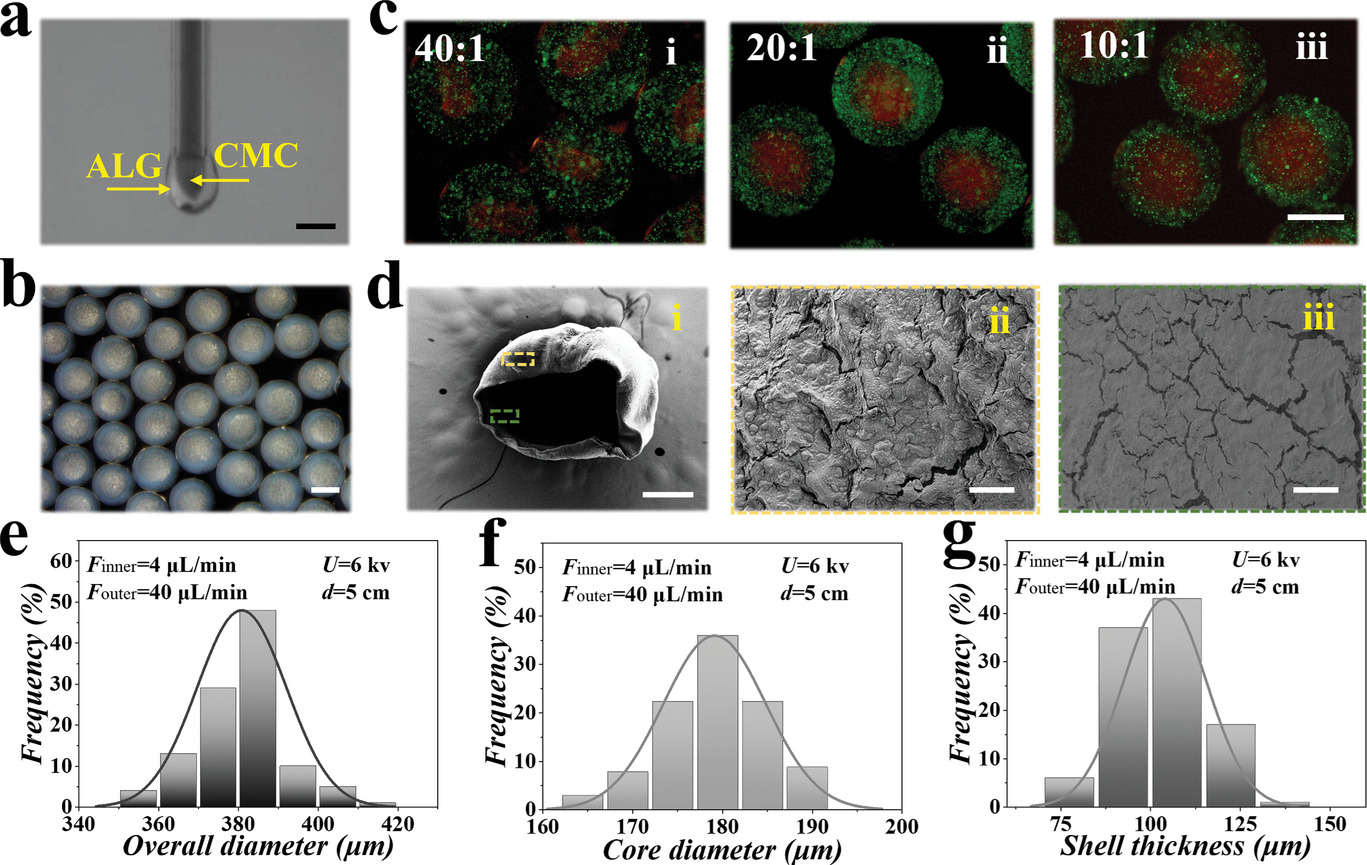
- (a)实时照片显示了CMC/ALG液滴的同轴生成。
- (b)体视镜下观察到均匀的核-壳结构水凝胶微胶囊。
- (c)不同流速比下生成的微胶囊的荧光图像。ALG和CMC的前体溶液分别与荧光聚苯乙烯纳米颗粒L4655(绿色)和L3280(红色)混合。
- (d)SEM图像之
- (i)冻干微胶囊;
- (ii)壳表面;
- (iii)核表面。
- (e)图中参数下CMC/ALG微胶囊的整体尺寸分布图。
- (f)图中参数下CMC/ALG微胶囊的核大小分布图。
- (g)图中参数下CMC/ALG微胶囊的壳厚度分布图。
Generation and characterization of tumor spheroids encapsulated in the hydrogel microcapsules
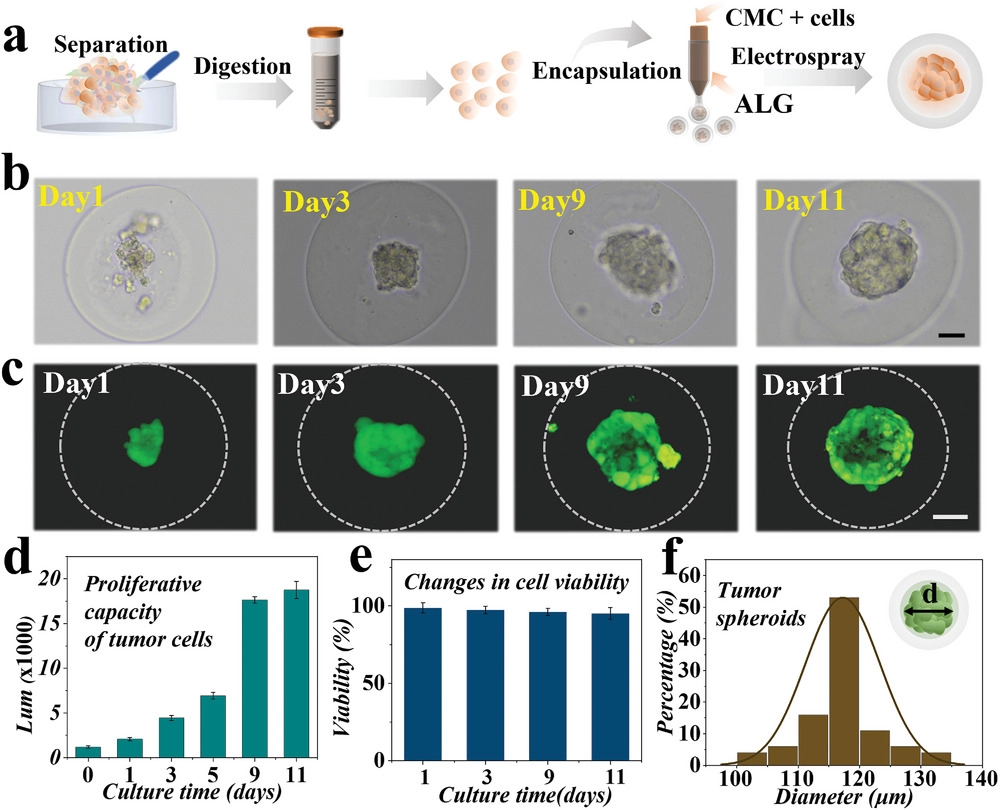
- (a)提取原代胰腺癌细胞和通过微流控电喷法准备装载细胞微胶囊的示意图。
- (b)原代胰腺癌细胞封装到微胶囊第1、3、9和11 d的白光图。
- (c)第1、3、9和11 d的微胶囊中肿瘤球细胞活死染色。
- (d)通过CellTiter-Glo 3D细胞活性测定法,对第1、3、9和11 d的肿瘤球的细胞增殖进行定量分析。纵坐标的Lum指的是发光信号(luminescent signal),它间接反映三磷酸腺苷(adenosine triphosphate,ATP)和细胞的数量。
- (e)第1、3、9和11 d的肿瘤球细胞活性的定量分析。以上显示了水凝胶微胶囊的出色的生物相容性,以及在6 kv电压的微流控电喷后,原代胰腺癌细胞仍然保持了良好的活性、增殖和分化能力。
- (f)第11 d的肿瘤球尺寸分布。结果表明,在微胶囊中培养的肿瘤球具有均匀的大小。
Concentration gradient generator and tumor spheroid surface characteristics and structure
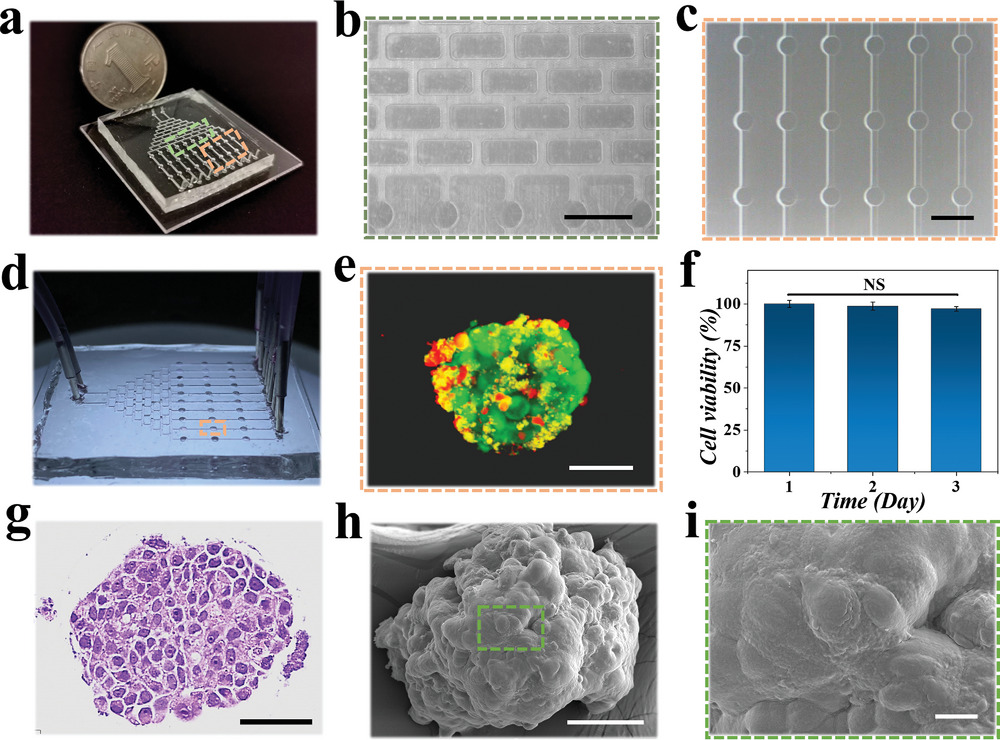
- (a)浓度梯度生成器的照片。
- (b)浓度梯度生成器的显微图像。
- (c)肿瘤球培养室的显微图像。
- (d)肿瘤球集成的微流控芯片的光学图像。
- (e)活/死染色后培养室中微囊包裹的肿瘤球的激光共聚焦扫描图像。
- (f)肿瘤球接种到培养室后第1、2、3 d的细胞活力定量分析
- (g)胰腺癌肿瘤球的HE染色图像。
- (h)一个完整的胰腺癌肿瘤球的SEM图像。
- (i)肿瘤球的表面结构的放大图像。
Histopathological features of the tumor spheroids

- (a)胰腺癌肿瘤球的CD44和MUC1的免疫荧光染色。
- (b)胰腺癌肿瘤球的MUC5AC和CD133的免疫荧光染色。
- (c)胰腺癌肿瘤球的Ki67和CK19的免疫荧光染色。
CD44,CD133:胰腺癌的肿瘤干细胞标志物。
MUC1,MUC5AC:粘液蛋白家族成员,用于胰腺癌的病理诊断。
CK19:胰腺导管上皮细胞相关。
Response of pancreatic tumor spheroids to antineoplastic agents

- (a)微流控浓度梯度发生器中形成的药物浓度梯度的数值模拟。显示了浓度梯度生成器的可靠性,适用于药物筛选。
- (b)药物溶液流经培养室的示意图。
- (c)药物在流动下渗透到微胶囊中的数值模拟(X轴为流体流动方向)。
- (d-f)取来自于三个胰腺癌患者的癌细胞构建肿瘤球,分别命名为PDA01、PDA02和PDA03。在芯片上进行药物处理之前,肿瘤球在微胶囊中连续培养9 d。
- (d)方案4(1 µM Gem处理4 h);
- (e)方案5(1 µM S-1: 5-FU + 吉美拉西gimeracil + 奥特拉西钾oteracil potassium联用,处理48 h);这两种方案下,三类肿瘤球没有显著差异。
- (f)方案6(GS: 脉冲剂量下的Gem和S-1,即4h Gem + S-1和44 h S-1);PDA02对GS有显著的耐药性(虽然不显著,对于Gem和S-1也表现出更高抗性)。通过设置这些药物浓度梯度,可以得到来自不同患者的肿瘤球的剂量反应曲线,并计算出IC50,从而更直观地比较不同患者个体的肿瘤球的药物敏感性差异。
- (g-h)PDA02患者在(g)术前、(h)术后和(i)肿瘤转移(第5个化疗周期时)阶段的计算机断层扫描数据。手后的长期临床随访研究显示,PDA02患者在接受5个周期的Gem和S-1化疗后出现多处转移,而PDA01和PDA03患者在接受8个周期的化疗后没有发现转移。这一结果表明,肿瘤球模型可以很好地保留原发肿瘤的异质性。
Clinical information for patients with pancreatic cancer corresponding to the three kinds of tumor spheroids
| Patient | Tumor site | Pathology | Differentiation | Chemotherapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDA01 | Heada | Ductal adenocarcinoma | Moderately | Gem+S-1 |
| PDA02 | Head | Ductal adenocarcinoma | Poorly | Gem+S-1 |
| PDA03 | Head | Ductal adenocarcinoma | Moderately | Gem+S-1 |
- a Head:胰头。
与PDA01和PDA03患者相比,PDA02患者的癌细胞分化较差,导致恶性程度较高。因此,PDA02患者更容易产生耐药性,更早出现肿瘤转移。
Conclusion
- 通过微流控电喷技术制造了具有CMC核和ALG壳的水凝胶微胶囊,用于三维肿瘤细胞的培养;
- 通过调节流体流速、电压和收集距离,能产生尺寸可调且均匀的水凝胶微胶囊。原代胰腺癌细胞能在微胶囊中迅速增殖,并形成三维肿瘤球,具有高度均匀的尺寸和良好的细胞存活率;
- 通过集成浓度梯度生成器,可以建立药物浓度梯度,用于动态和高通量地筛选不同的化疗方案;
- 实验结果显示,来自不同病人的胰腺癌肿瘤球对同一药物表现出异质性的药物敏感性,这与手术后从相应病人那里获得的临床数据一致;
- 这些结果表明,目前的微流控集成肿瘤球平台在临床药物评估方面很有前景,可以为个性化治疗带来启示。
Reference
Song T, Zhang H, Luo Z, et al. Primary Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells Cultivation in Microfluidic Hydrogel Microcapsules for Drug Evaluation[J]. Advanced Science.



